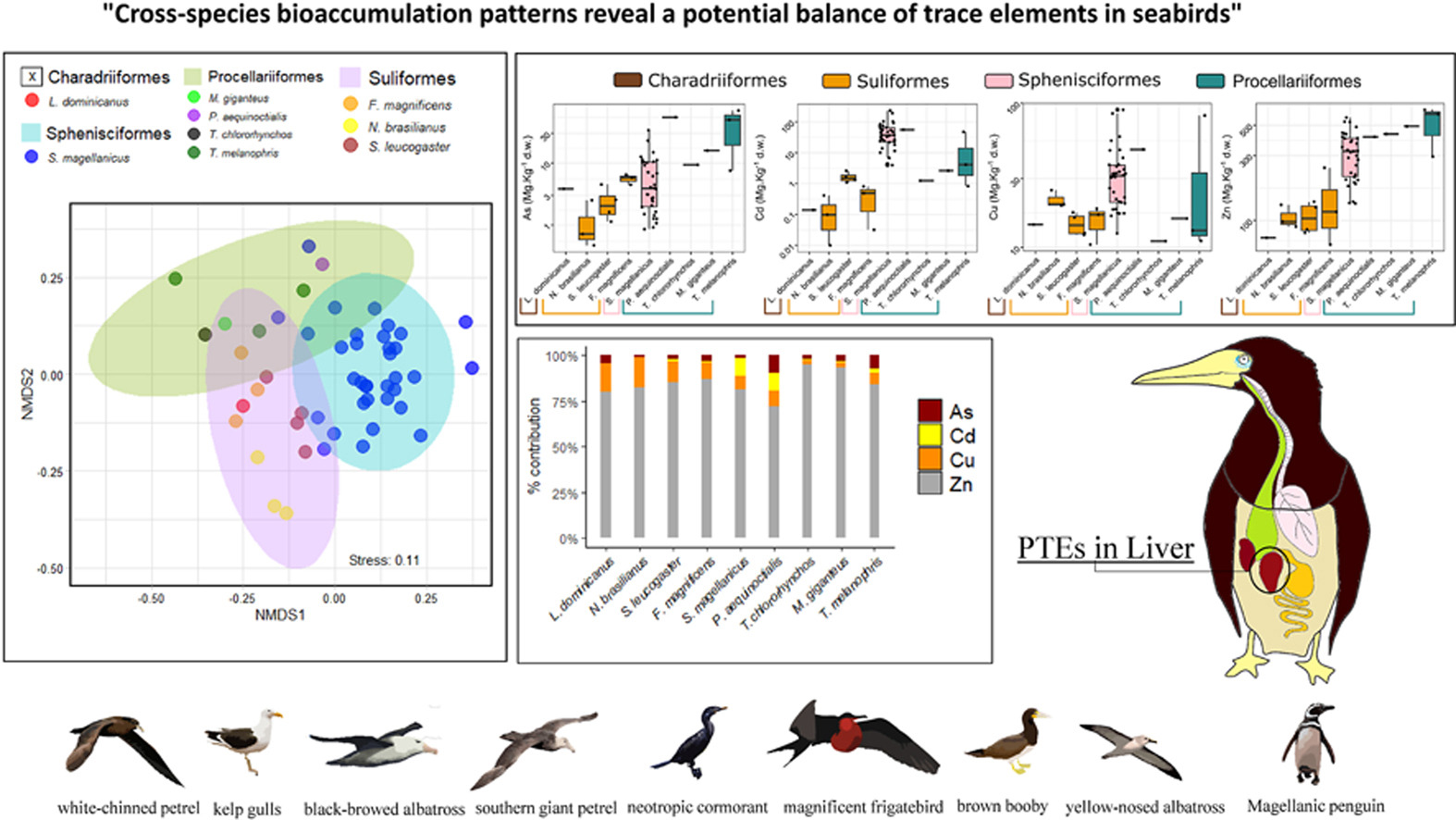
The publication’s graphical abstract
Guilherme dos Santos Lima (Environmental Studies Center, São Paulo State University, Rio Claro, Brazil) and colleagues have published in the journal Environmental Pollution on levels of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in seabirds from the south-western Atlantic Ocean, including Atlantic Yellow-nosed Thalassarche chlororhynchos and Black-browed T. melanophris Albatrosses and Southern Giant Macronectes giganteus and White-chinned Procellaria aequinoctialis Petrels.

A Southern Giant Petrel guards its chick, artwork by Leigh Wolfaardt
The paper’s abstract follows:
“Seabirds are particularly susceptible to potentially toxic elements (PTEs) due to the tendency of biomagnification of some elements, thus serving as potential bioindicators for assessing environmental health. In this study, we analyzed As, Cd, Cu and Zn concentrations in liver samples from nine seabird species (51 specimens) collected along the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Results revealed substantial variations in PTE concentrations among species, with taxonomic orders influencing accumulation patterns. The observed PTE concentrations in seabirds suggest potential trends in bioaccumulation, influenced by species-specific behaviors and diets. For instance, As ranged from 0.47 mg kg−1 in Nannopterum brasilianus to 70.25 mg kg−1 in Thalassarche melanophris, while Cd ranged from 0.01 mg kg−1 in N. brasilianus to 232.73 mg kg−1 in Spheniscus magellanicus. Generalized Linear Model (GLM) results identified body length and species as the main factors influencing PTE concentrations for most elements. Spearman correlation analysis revealed a strong positive correlation between Cd and Cu (ρ = 0.68), Cd and Zn (ρ = 0.67) and between Zn and Cu (ρ = 0.56), suggesting that seabirds with higher Cd levels also tend to have higher Cu and Zn concentrations. Multivariate statistical analysis demonstrated distinct PTE compositions among bird groups. Although significant variations in total concentrations of elements like Zn and Cu were observed among species, the relative contributions of each element to the overall load in the organism showed a convergence in proportions. This underscores the need for further research on homeostatic processes and the potential impacts of environmental PTEs on seabird health.”
With thanks to Patricia Serafini.
Reference:
dos Santos Lima, G., Suarez, C.A., Gemeiner, H., Serafini, P.P., Alves de Deus, J.P., Viana, J.L.M. & Menegario, A.A. 2025. Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in seabirds foraging across a heterogeneous landscape: cross-species bioaccumulation patterns. Environmental Pollution 367. 125609.
John Cooper, Emeritus Information Officer, Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels, 09 January 2025

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español